Direct Superior Total Hip Replacement
The Direct Superior Approach is a minimally invasive surgical technique used in total hip replacement that allows the surgeon to access the hip joint while minimizing damage to the iliotibial (IT) band and surrounding muscles. This approach is designed to help patients experience a smoother recovery and return to activity more quickly.
Understanding Your Hip Pain
Every patient’s hip pain is different, and understanding the underlying cause is an important first step. Hip pain may result from:
- Arthritis
- Degeneration of cartilage
- Bone damage
- Hip deformities
- Injury or overuse
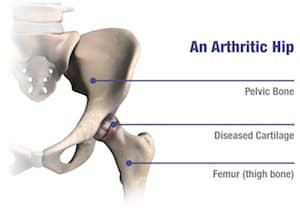
Arthritis is one of the most common causes of chronic hip pain. As cartilage wears away, the bones begin to rub together, causing inflammation, stiffness, and loss of mobility. If pain persists despite medications, physical therapy, or other conservative treatments, hip replacement may be recommended.
Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement involves removing the arthritic portions of the joint and replacing them with smooth, durable implants. The hip is a ball-and-socket joint, consisting of:
- The femoral head (ball) at the top of the thighbone
- The acetabulum (socket) in the pelvis
During surgery:
- The femoral head is replaced with a metal stem and artificial ball
- The acetabulum is reconstructed with a metal cup and a durable plastic liner
- These components work together to restore smooth, pain-free movement
Direct Superior Approach
The Direct Superior Approach is a minimally invasive option used during total hip replacement. This technique may be associated with:
- Reduced muscle damage
- Smaller incisions
- Improved early recovery
- Preservation of key soft-tissue structures
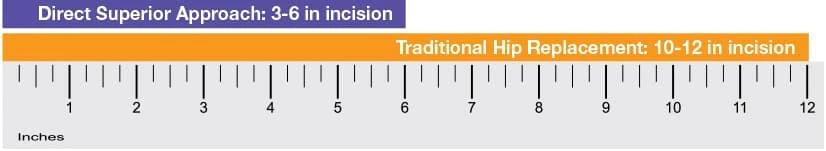
One key difference is the location and orientation of the incision. Traditional hip replacement often requires an incision through the IT band. In the Direct Superior Approach, the surgeon avoids cutting the IT band, which may reduce postoperative soreness and protect important hip stabilizers.
Typical incision size:
- Traditional approach: 10 to 12 inches
- Direct Superior Approach: 3 to 6 inches
Important Information for Hip Replacement Patients
Hip replacement surgery is intended for individuals with joint damage caused by:
- Degenerative arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Avascular necrosis
- Hip fractures
- Functional deformity
Hip replacement may not be appropriate for patients with severe infection, certain neuromuscular disorders, compromised bone quality, skeletal immaturity, or excessive body weight. Your surgeon will review your medical history and determine whether you are a safe candidate for surgery.
Surgical Risks
All surgeries carry risks. Potential risks of hip replacement include:
- Pain or stiffness
- Bone fracture
- Nerve injury
- Blood clots
- Infection
- Leg length changes
- Implant loosening or wear
- Reaction to implant materials
- Need for revision surgery
Your surgeon will discuss ways to minimize these risks and explain how to protect your new hip over time.
Recovery and Long-Term Expectations
Most hip replacement patients begin walking with assistance shortly after surgery. Physical therapy focuses on:
- Maintaining safe range of motion
- Regaining strength
- Restoring normal walking patterns
Activity levels and recovery timelines vary by patient. Many resume daily activities within several weeks. Your surgeon will provide follow-up care and guidance to help prolong the life of your hip replacement.
References
- Roger, D. J., & Hill, D. (2012). Minimally Invasive Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a Transpiriformis Approach: A Preliminary Report. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 470(1).
- Penenberg BL, Bolling WS, Riley M. Percutaneously assisted total hip arthroplasty (PATH): a preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(suppl 4):209–220
- Khan RJ, Fick D, Khoo P, Yao F, Nivbrant B, Wood D. Less invasive total hip arthroplasty: description of a new technique. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:1038–1046.
- AAOS website, http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=a00404, accessed March 2016.
GSNPS-PE-65_10857
Copyright © 2016 Stryker Corporation
Back to Hip







